Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) technologies are transforming the way industries deliver job-specific training. These immersive technologies enable realistic simulations, providing hands-on experience without the associated risks. In sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and aviation, where precision, safety, and expertise are critical, VR/AR/MR offer innovative and effective training solutions.
1. Manufacturing
Training workers for complex machinery operations or hazardous environments requires a blend of theory and practice. VR and AR allow manufacturers to simulate factory environments, enabling employees to practice operating equipment, assembly procedures, and safety protocols without real-world risks.
- Global Use Case: Volkswagen uses VR to train employees on assembling vehicles, enhancing safety and efficiency while reducing errors in production.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, job-specific roles like surgery, diagnostics, and patient care demand exceptional accuracy. VR/AR technologies enable trainees to practice complex procedures in a risk-free, controlled environment. MR, in particular, allows blending virtual anatomy with real-world instruments, making training more interactive and practical.
- Global Use Case: Cleveland Clinic and Case Western Reserve University use AR to teach anatomy through 3D holograms, making medical education more interactive and improving comprehension.
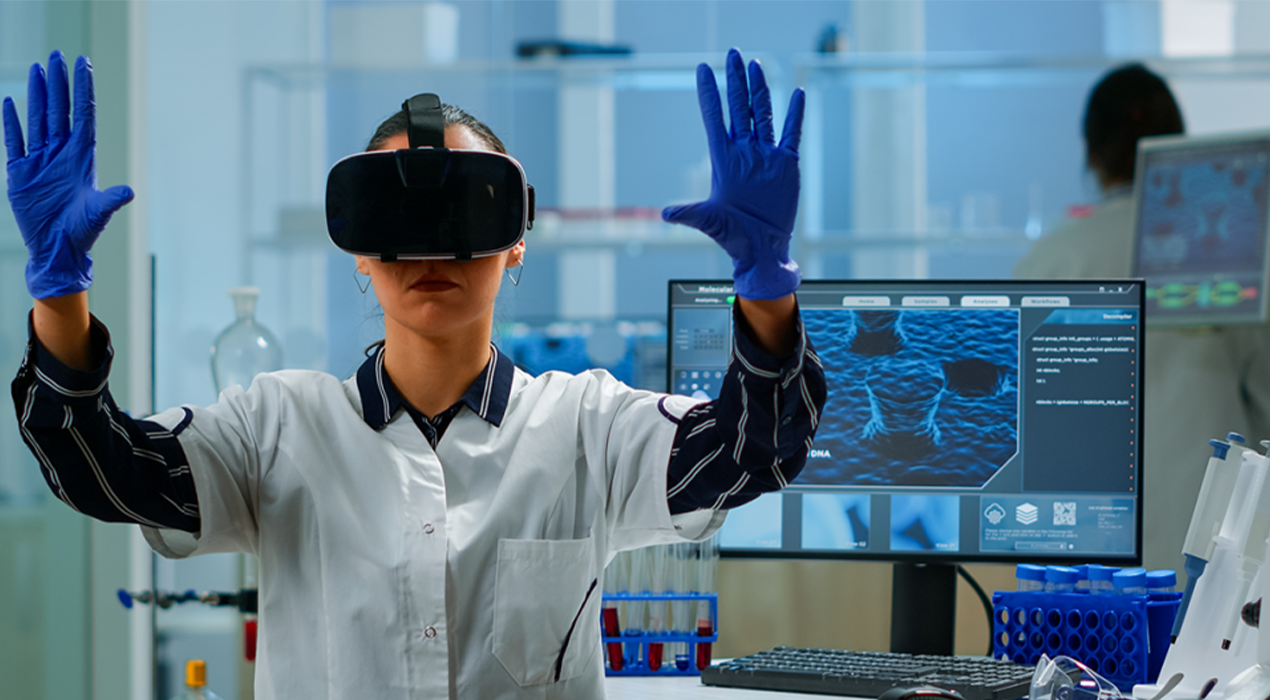
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical sector, especially in critical roles such as drug manufacturing, quality control, and regulatory compliance, requires precise handling of materials and processes. VR/AR training can simulate cleanroom environments and complex workflows, ensuring employees follow rigorous standards without risking contamination.
- Global Use Case: Pfizer uses VR to train its workforce in complex laboratory environments, ensuring adherence to stringent safety and procedural guidelines while reducing the costs and risks of real-world training.
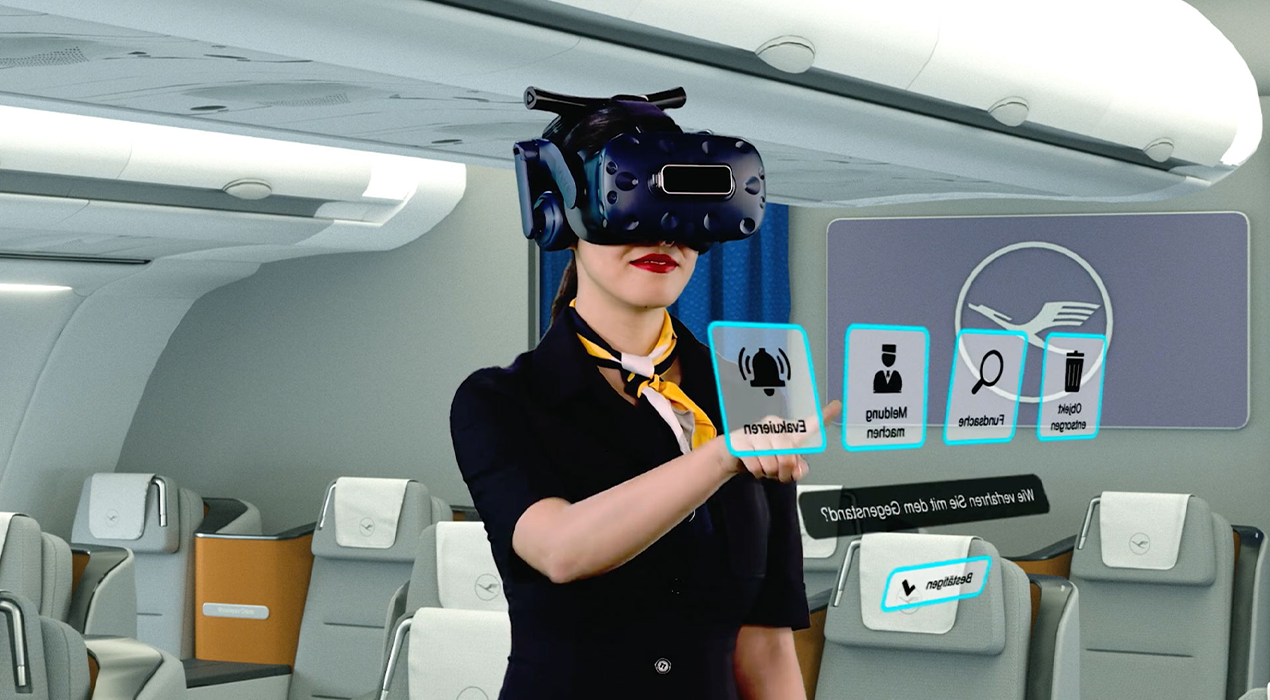
4. Aviation and Airport Ground Staff
In aviation, where safety and precision are paramount, VR/AR is used to train pilots, engineers, and ground crew. Simulated flight experiences allow pilots to handle emergencies and complex scenarios, while AR can provide real-time guidance to ground staff on aircraft maintenance, loading, and refueling operations.
- Global Use Case: Lufthansa Aviation Training uses VR to train pilots and cabin crew for emergency procedures and safety protocols, improving preparedness while reducing the need for expensive physical simulators.
Conclusion
VR/AR/MR technologies provide immersive, risk-free environments for job-specific training across diverse industries. Their ability to simulate complex, real-world scenarios makes training more efficient, cost-effective, and safe. By embracing these technologies, industries are enhancing the skillsets of their workforce, ensuring higher productivity and adherence to safety standards.
The future of training is immersive, and these technologies are leading the way globally.